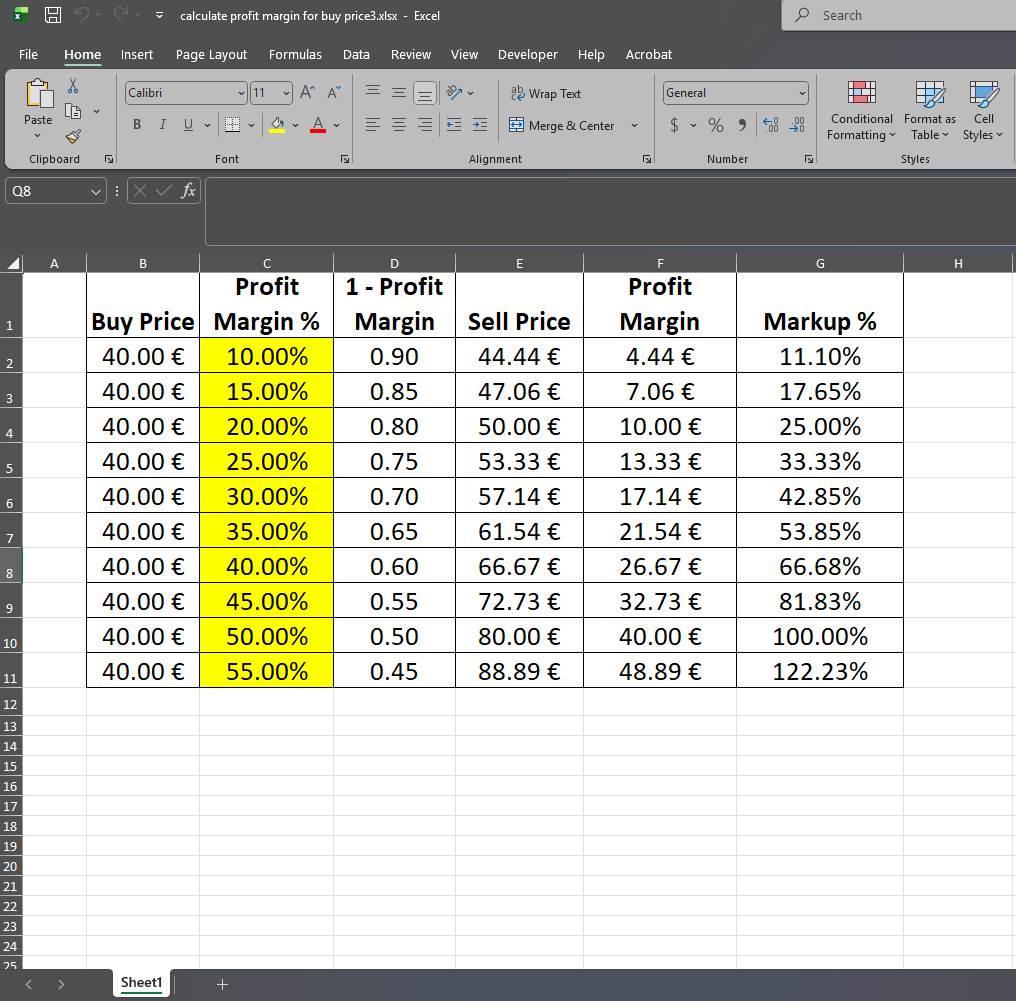
✅ Understanding Profit Margin, Markup, and Selling Price (With Example Table) When you run a business, knowing how to correctly price your products is essential. Two of the most common pricing metrics are profit margin and markup. Although people often mix them up, they are not the same thing. Let’s break it down using the example above, where every product has a €40.00 buy cost. ✅ 1. Profit Margin % Profit margin shows how much profit you earn as a percentage of the selling price. Example: Buy Price: €40.00 Profit Margin: 25% Sell Price becomes €53.33 Profit earned: €13.33 Formula: Sell Price = Buy Price / (1 − Profit Margin) ✅ 2. Sell Price This is the final price you charge the customer after applying the profit margin. You can see how the selling price increases as the margin goes up. Example: 10% margin → €44.44 selling price 40% margin…
Charts to easily convert between Gross Profit Margin and Markup as you estimate costs and pricing for individual jobs. Όταν υπολογίζετε τιμές διάθεσης-πώλησης μην ξεχνάτε ότι το Gross Profit Margin (Μικτό Περιθώριο Κέρδους) είναι αυτό που σας ενδιαφέρει και όχι το MarkUp. Φωτογραφία 1 Αν θέλουμε να πουλήσουμε κάτι που αγοράσαμε 100€ με 20% κέρδος (gross profit margin) πρέπει να πληκτρολογήσουμε στο κομπιουτεράκι μας100 * 25% (markup) = 125Τόσο πρέπει να το πουλήσουμε αν θέλουμε να έχουμε 20% κέρδος.Εάν σε αυτήν την τιμή πώλησης-διάθεσης δηλ. το 125 αφαιρέσουμε το 20%, δηλαδή125 – 20% (gross profit margin) = 100, μας δίνει το 100, όσο δηλαδή όσο το αγοράσαμε. Ως μικτό περιθώριο κέρδους – Gross Profit Margin θεωρείται το ποσοστό που εξάγεται από τον εξής τύπο:(Τιμή Πώλησης – Τιμή αγοράς) / Τιμή πώλησηςΣτο παράδειγμα μας (125-100)/125 = 25/125 = 0,2 δηλαδή μικτό περιθώριο κέρδους – Gross Profit Margin 20% και όχι 25%…